After determining the audit risk identification using BP neural network, support vector machine, and random forest methods, the samples are fed into the identification model for training identification according to a certain process. As a machine learning method, the support vector machine algorithm is based on the statistical theory of VC dimensionality and the theory of structural risk minimization to solve constrained quadratic planning problems. SVM theory is widely used in pattern classification and nonlinear regression, mainly to solve the problem of identifying nonlinear, multidimensional data, especially under small sample conditions.
- Unlike in the existing literature, the selection of the optimal scales and reduction are simultaneously performed in the viewpoint of local and global approximations in dominance-based multi-scale IF decision tables.
- Low audit risk is significant as auditors can’t verify every transaction.
- A random function is used to group the sample data into two parts, the training set and the testing set, and to generate the corresponding label sets, the former for model learning and training, and the latter for model testing.
- Lower detection risk may be achieved by increasing the sample size for audit testing.
The audit risk model has certain limitations, including subjectivity, limited scope, and the risk of incomplete information, which auditors must be aware of when using this tool. Cuts down on the human error element of audit risk, saving time and money. GoCardless integrates with over 350 partners, recording transactions at the point of payment to improve accuracy and streamline the accounting workflow. Inherent risk is based on factors that ultimately affect many accounts or are peculiar to a specific assertion. For example, the inherent risk could potentially be higher for the valuation assertion related to accounts or GAAP estimates that involve the best judgment. The audit risk model is best applied during the planning stage and possesses little value in terms of evaluating audit performance.
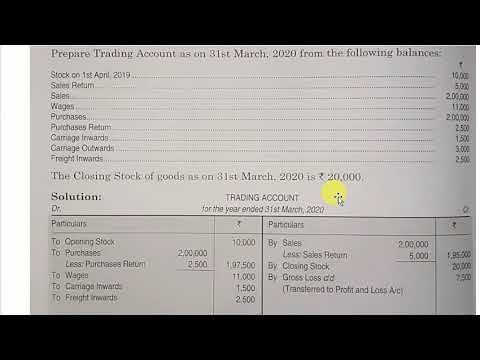
Audit Risk Model for Planning
Auditors decrease detection risk—the risk that material misstatements will not be detected—by appropriately planning and performing their work. Audit failure occurs when an audit firm issues an unmodified opinion and the financial statements are not fairly stated. A material misstatement is present and the auditor doesn’t know it.
Since some transactions are more prone to theft or error, companies need internal controls to prevent or detect misstatements. The audit firm issues an unmodified opinion but the financial statements are not fairly stated. Audit risk assessment at the onset of the audit procedure is an integral part of the audit procedure.
Three audit risk identification models are built using support vector machines, BS neural networks, and random forest methods. BP neural networks are used in a wide range of fields such as medicine , economics , and, in recent years, in the field of auditing . In relating the components of audit risk, the auditor may express each component in quantitative terms, such as percentages, or-non-quantitative terms such as very low, low, moderate, high, and maximum.
Audit Risk Model
A secondary objective of the discussions is to set a proper tone for the engagement. A highly centralized organizational structure generally has all significant computerized processing controlled and supervised at a central location. Auditors can obtain most of the necessary computerized processing information by visiting the central location. Related parties include those individuals or organizations that can influence or be influenced by decisions of the company, possibly through family ties or investment relationships.
Notice of Climeon Ab (Publ) 2023 Annual General Meeting – Marketscreener.com
Notice of Climeon Ab (Publ) 2023 Annual General Meeting.
Posted: Thu, 13 Apr 2023 05:31:08 GMT [source]
The mixed approach used in the case study can be employed by practitioners to select an optimal delivery method for other construction programs. To deal with these risk assessment issues, various methods have been used individually or combined with others. Indeed, the selection of appropriate risk assessment approach with a consideration of specific features of different industry and different requirement is one crucial step for risk management .
Auditor Industry Specialization and Discretionary Accruals: The Role of Client Strategy
Explain in detail the inherent risk factors that are involved while assessing the risks for the intangible assets. Explain why an audit of internal controls provides value to the investing public. Describe circumstances that might cause the auditors to identify understatement of assets as a significant audit risk. Control risk – Risk that the misstatement will not be prevented, or detected and corrected on a timely basis by the entity’s internal control. It’s worthwhile to review how an organisation is handling its controls by reviewing its financial reporting processes, control activities, communication and monitoring abilities. Auditors will consider how much emphasis a business places on accurate financial reporting, the ways by which information is monitored and its day-to-day activities.

Audit model is the technique used by the auditor at the time of audit planning to manage the risk in audit performance. Audit model indicate the level of risk that may be involved in conducting audit. Audit Model facilitates analysis of all such risks help the auditor to decide the required audit procedures and techniques to be adopted to eliminates or minimize Audit Risk. With this information, an auditor can then apply the risk model to see how much emphasis must be placed on detection risk. For example, given a high control and inherent risk, then an auditor will need to perform more substantive tests to lessen detection risk. If the opposite is true, then detection risk could be relatively low and so the auditor’s process will be less intensive.
accounting equation risk exists no matter who conducts an audit report or the type of company providing the financial statements. However, there are ways to help manage and reduce audit risk. The audit risk matrix provides a visual representation of the risk assessment.
The increased use of big data and analytical tools has the potential to improve the effectiveness of this type of risk assessment procedure. Errors are unintentional misstatements or omissions of amounts or disclosures in financial statements. Auditors are required by professional standards to hold a brainstorming session to consider the risk of fraud in every audit engagement. Such as the use of sampling for the selection of transactions.Detection risk can be reduced by auditors by increasing the number of sampled transactions for detailed testing. O. Tamimi, “The role of internal audit in risk management from the perspective of risk managers in the banking sector,” Australasian Business, Accounting & Finance Journal, vol.
Prior to joining the RSM Executive Office in March 2012, Bob served as the RSM US LLP’s Director of Assurance Services and International Assurance Services Practice Leader and served a broad range of clients. Bob has twenty-nine years of experience in public accounting, all with RSM and McGladrey. Nature of the client – Make sure to think about business operations, investment and financing activities, and financial reporting. These three risks are multiplied together to calculate overall audit risk, or the risk of an auditor drawing inaccurate conclusions.
- Auditors can obtain most of the necessary computerized processing information by visiting the central location.
- Bob has twenty-nine years of experience in public accounting, all with RSM and McGladrey.
- Inherent risk is generally considered higher where a high degree of judgment and estimation is involved, or entity transactions are highly complex.
- Periodically, the AICPA staff, in consultation with the Auditing Standards Board, issues audit risk alerts.
An audit risk model is a conceptual tool applied by auditors to evaluate and manage the various risks arising from performing an audit engagement. The tool helps the auditor decide on the types of evidence and how much is needed for each relevant assertion. The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 states that when auditors believe an illegal act that is more than “clearly inconsequential” has or may have occurred, the auditors must inform the organization’s board of directors. When the auditors believe the illegal act has a material effect on the financial statements, the board of directors has one business day to inform the SEC.
Conversely, if https://1investing.in/ and control risks are assessed as low, the auditor may be able to perform less extensive audit procedures, resulting in a lower overall audit risk. The auditor must assess each component to determine an appropriate level of audit risk and design and execute audit procedures that address the identified risks. The ultimate goal is to obtain sufficient and appropriate audit evidence to support the auditor’s opinion on the fairness of the financial statements. Generally, an auditor will perform a control risk assessment concerning the financial statement level of risk and the assertion level of risk. Therefore, performing such an assessment will require the auditor to possess a strong understanding of the organization’s internal controls.
California homeless: Cities want $3 billion – CalMatters
California homeless: Cities want $3 billion.
Posted: Thu, 13 Apr 2023 12:03:54 GMT [source]
Frauds involving senior managers or employees with significant internal control roles should be reported directly to those charged with governance, usually the entity’s audit committee of its board of directors. According to auditing standards, analytical procedures must be applied in the preliminary stages of each audit. Auditors use analytical procedures to identify potential problem areas so that subsequent audit work can be designed to reduce the risk of missing something important. At this stage, analytical procedures are reasonableness tests; auditors compare their expectation for each of the account balances with those recorded by management. Describe management’s responsibility regarding audited financial statements.
Explain what we mean by the terms relevance and reliability, as the terms relate to audit evidence. Explain the meaning of relevance and reliability as the terms relate to audit evidence. Explain the characteristics and the internal control features of an imprest fund. Understand what a financial audit is, identify the purpose of a financial audit, and learn how to conduct a financial audit. Explain why the allowance for doubtful accounts is a “high risk” audit area.